國立臺灣師範大學中國信託成癮防制暨政策研究中心李思賢主任參與美國國家藥物濫用研究院主辦之2022藥物濫用研究國際論壇(2022 NIDA International Forum),並發表多篇海報發表。
本中心李思賢主任、趙恩博士與法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心合作之110年度毒品防制基金「毒品施用行為多元處遇成效評估與比較計畫:第四期」研究案成果,已共同於美國國家藥物濫用研究院(NIDA)舉辦之2022年國際研討會進行海報發表。本次發表通過NIDA審查,內容為以機器學習模型完成緩起訴附命戒癮治療者在追蹤1、2、5年內不再施用毒品之機率結果。經雙方努力,共同於國際學術論壇上將研究成果發光發熱,恭喜研究團隊!
發表作者(以貢獻度排名):
國立臺灣師範大學中國信託成癮防制暨政策研究中心 趙恩
法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心 顧以謙
法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心、中央研究院法律學研究所 鍾宏彬
法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心 許家毓
法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心 鄭元皓
法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心 許茵筑
法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心 蔡宜家
國立臺灣師範大學中國信託成癮防制暨政策研究中心、國立臺灣師範大學健康促進與衛生教育學系,通訊作者 李思賢
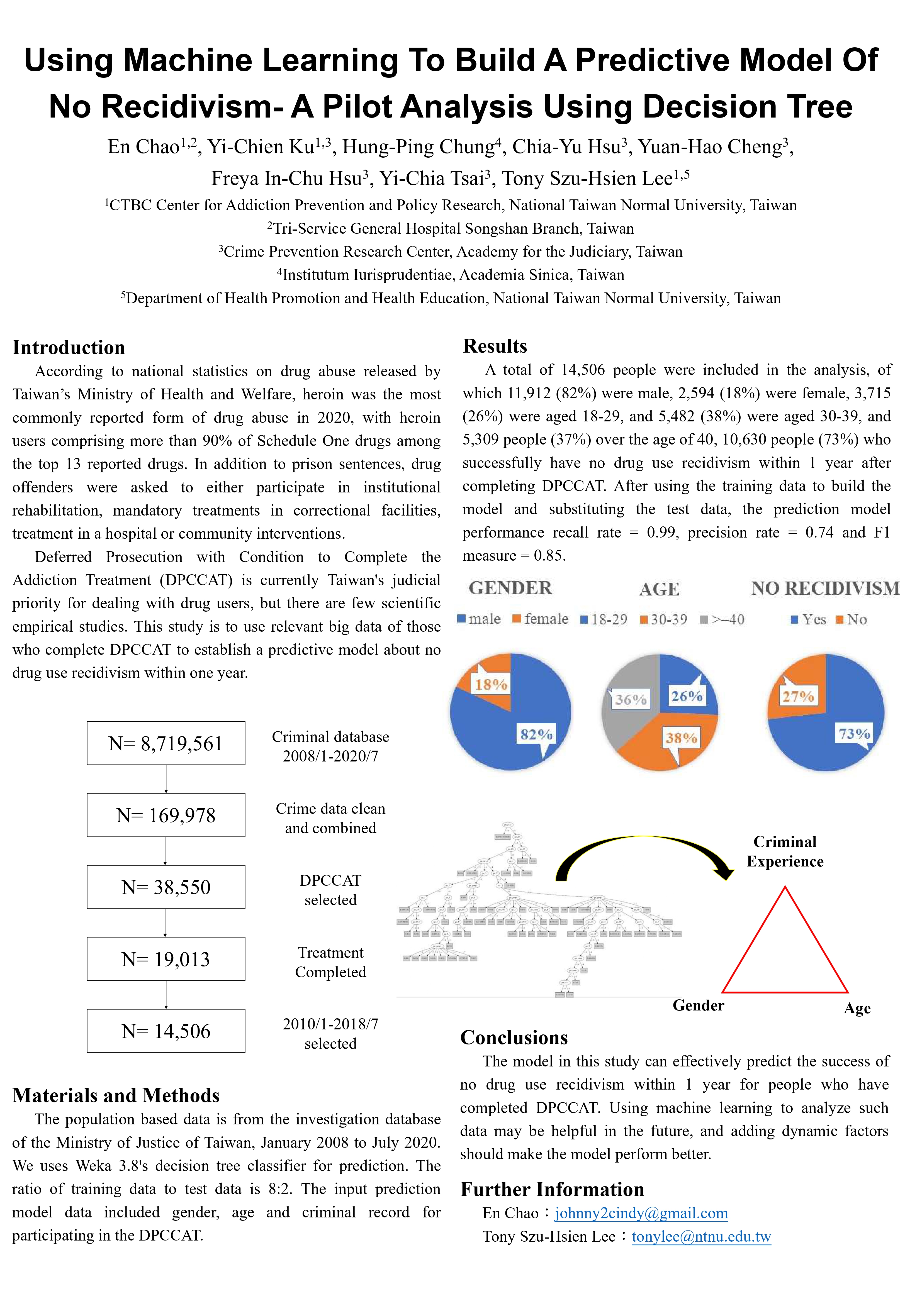
一、Using Machine Learning to Build a Predictive Model of No Recidivism- A Pilot Analysis Using Decision Tree(以機器學習建置不再犯之預測模型-決策樹分析之先導研究)
此研究與中國信託成癮防制暨政策研究中心趙恩資料長、中央研究院博士後研究學者鍾宏彬及法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心研究團隊共同進行海報發表。
En Chao, Yi-Chien Ku, Hung-Ping Chung, Chia-Yu Hsu, Yuan-Hao Cheng, Freya In-Chu Hsu, Yi-Chia Tsai, Tony Szu-Hsien Lee (2022, Jun). Using Machine Learning to Build a Predictive Model of No Recidivism- A Pilot Analysis Using Decision Tree. NIDA International Poster Session, No. 70, Virtual Scientific Meeting, 2022 NIDA International Forum, June 9-10, 2022.
Abstract
Background: Deferred Prosecution with Condition to Complete the Addiction Treatment (DPCCAT) is currently Taiwan's judicial priority for dealing with drug users, but there are few scientific empirical studies. This study is to use relevant big data of those who complete DPCCAT to establish a predictive model about no drug use recidivism within one year.
Methods: The population based data is from the investigation database of the Ministry of Justice of Taiwan, January 2008 to July 2020. We uses Weka 3.8's decision tree classifier for prediction. The ratio of training data to test data is 8:2. The input prediction model data included gender, age and criminal record for participating in the DPCCAT.
Results: A total of 14,506 people were included in the analysis, of which 11,912 (82%) were male, 2,594 (18%) were female, 3,715 (26%) were aged 18-29, and 5,482 (38%) were aged 30-39, and 5,309 people (37%) over the age of 40, 10,630 people (73%) who successfully have no drug use recidivism within 1 year after completing DPCCAT. After using the training data to build the model and substituting the test data, the prediction model performance recall rate = 0.99, precision rate = 0.74 and F1 measure = 0.85.
Conclusions: The model in this study can effectively predict the success of no drug use recidivism within 1 year for people who have completed DPCCAT. Using machine learning to analyze such data may be helpful in the future, and adding dynamic factors should make the model perform better.
二、Polydrug Use Could Affect Outcomes of Treatment with BDRC in Opiate Use Patients(多重藥物使用對於BDRC藥癮治療之療效影響分析)
此研究與美國賓州大學愛滋病預防研究中心主任David S. Metzger,以及中國疾病預防控制中心馬麗英教授、法務部司法官學院犯罪防治研究中心顧以謙研究員共同進行海報發表,研究發現指出多重藥物濫用行為會對以buprenorphine/naloxone藥物合併行為之治療的療效造成損害。
Yi-Chien Ku, Tony Szu-Hsien Lee, Ma, L., David S. Metzger (2022, Jun). Polydrug Use Could Affect Outcomes of Treatment with BDRC in Opiate Use Patients. NIDA International Poster Session, No. 116, Virtual Scientific Meeting, 2022 NIDA International Forum, June 9-10, 2022.
Abstract:
Background: HPTN058 was a randomized trial aimed to evaluate the efficacy of a medication-assisted treatment (MAT) strategies combined with behavioral drug and risk counseling (BDRC) for opioid injectors at high risk of HIV infection. In the literature, polydrug usage has garnered considerable attention due to its negative effects on treatment outcomes. To understand the factors associated with successful reduction in opioid use in HPTN 058, we examined demographics, polydrug use, and participation in counseling as potential predictors of treatment outcomes.
Method: People who inject drugs (PWID) were enrolled at sites in Nanning and Heng County in Guangxi, China, Xinjiang, China, and Chiang Mai, Thailand. This study included participants who were randomized to 3 times per week dosing with buprenorphine/naloxone and 12 months of counseling (LT-MAT). Assessments for non-injection (NIP) and injection polydrug (IP) use for the past month. Assessments took place at baseline, 6-, 12-, 18-, and 24 months post enrollment.
Results: We analyzed data from 623 participants assigned to the long-term treatment arm. Participants were mostly males (92.1%) and had an average age of 34.41 (SD=8.05), 3.6%-22.9% reported NIP, 0.5-3.8% reported IP, and 0.5-9.3% reported marijuana use. The average number of counseling sessions was 16.4 of a possible 21 sessions. Overall, there was a significant decrease in opiate use over the study period. However, there is no significant difference in opioid use between NIP and IP at baseline, 6-, 18-, and 24 months. After we controlled for age, gender, follow-up periods, and non-injection drug use, the results from the negative binomial regression (NBR) model found that the relationship between participation in counseling and opiate use was negatively moderated by IP (OR= 1.058, 95% CI: 1.02–1.1). The interaction between marijuana use and participation in counseling has an approximately 4.4% lower odds of opiate use (OR= 1.044, 95% CI: 1.02–1.07).
Conclusion: The findings showed that IP (injecting multiple drugs) moderates the effects of MAT and counseling in reducing opiate use. Future evaluation for MAT for OUD should take polydrug use into consideration. Further, marijuana use was associated with positive MAT outcomes. Future research is necessary to confirm and understand the role of marijuana use in buprenorphine treatment of opioid use disorder.

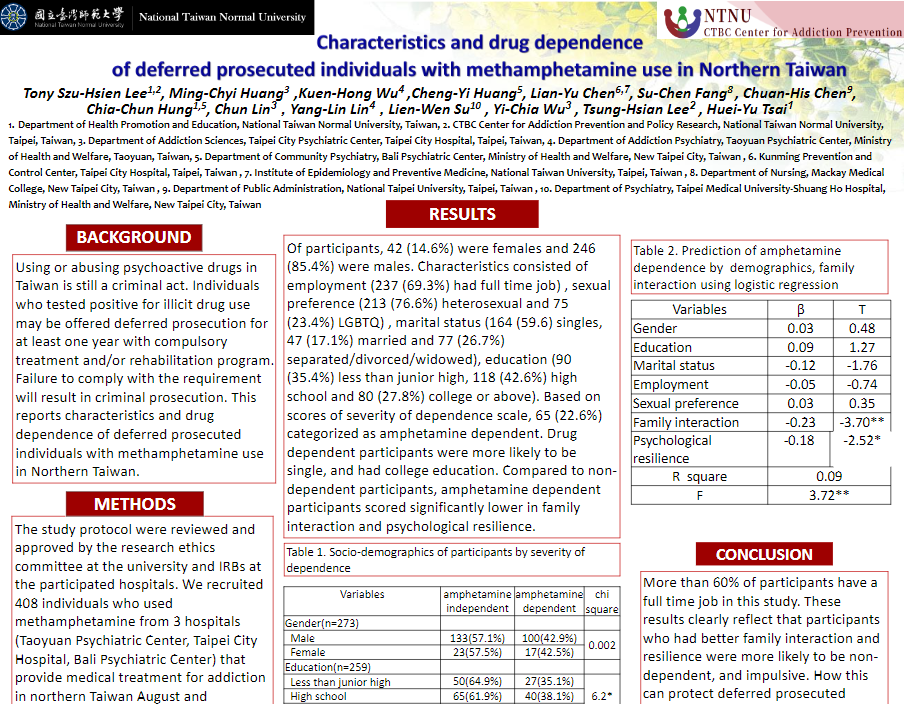
三、Characteristics and drug dependence of deferred prosecuted individuals with methamphetamine use in Northern Taiwan(北臺灣緩起訴附命戒癮治療者施用安非他命之特性與成癮)
此研究與台北市聯醫松德院區成癮防治科主任黃名琪、衛生福利部桃園療養院成癮治療科吳坤鴻主任等人聯名發表,研究發現罹患嚴重興奮劑使用疾患者更有可能是LGBTQ、單身和擁有大學教育,且罹患嚴重興奮劑使用疾患者在家庭互動和心理復原力明顯較低,此點顯示具有較好的家庭互動和復原力者較可能有較低嚴重程度興奮劑使用障礙。
Using psychoactive drugs in Taiwan is a criminal act. Individuals who test positive for drug use may be offered deferred prosecution for at least one year with compulsory treatment. Here we report on the sociodemographic and substance use characteristics of individuals with methamphetamine use. We recruited 288 individuals who used methamphetamine from hospitals that provide addiction treatment in northern Taiwan between August and December 2021. Participants self-reported a questionnaire that consists of measures of gender, education, sexual preferences, marital status, family relations, impulsivity, psychological resilience, severity of dependence, and emotional regulation. In assessing the severity of substance use disorder, 65 (22.6%) participants were categorized as severe. Of participants, 42 (14.6%) were female and 246 (85.4%) were male. Other characteristics assessed included: employment (237 (69.3%) had full time job); sexual preference (213 (76.6%) heterosexual and 75 (23.4%) LGBTQ); marital status (164 (59.6) single, 47 (17.1%) married and 77 (26.7%) separated/divorced/widowed); and, education (90 (35.4%) less than junior high, 118 (42.6%) high school and 80 (27.8%) college or above). Participants with severe stimulant use disorder were more likely to be LGBTQ, single, and had college education. Compared to other participants, those with severe stimulant use disorder scored significantly lower in measures of family interaction and psychological resilience. These results strongly suggest that participants who had better family interaction and resilience were more likely to have less severe stimulant use disorder. The protective effects of family interaction and resilience among stimulant users participating in the deferred prosecution program will be discussed further.
Tony Szu-Hsien Lee, Ming-ChyiHuang, Kuen-Hong Wu ,Cheng-Yi Huang, Lian-Yu Chen, Su-Chen Fang, Chuan-His Chen, Chia-Chun Hung, Chun Lin, Yang-Lin Lin, Lien-Wen Su, Yi-Chia Wu, Tsung-Hsian Lee, Huei-Yu Tsai. (2022, Jun). Characteristics and drug dependence of deferred prosecuted individuals with methamphetamine use in Northern Taiwan, No. 117, Virtual Scientific Meeting, 2022 NIDA International Forum, June 9-10, 2022.
nida-poster-guide-2022.pdf
